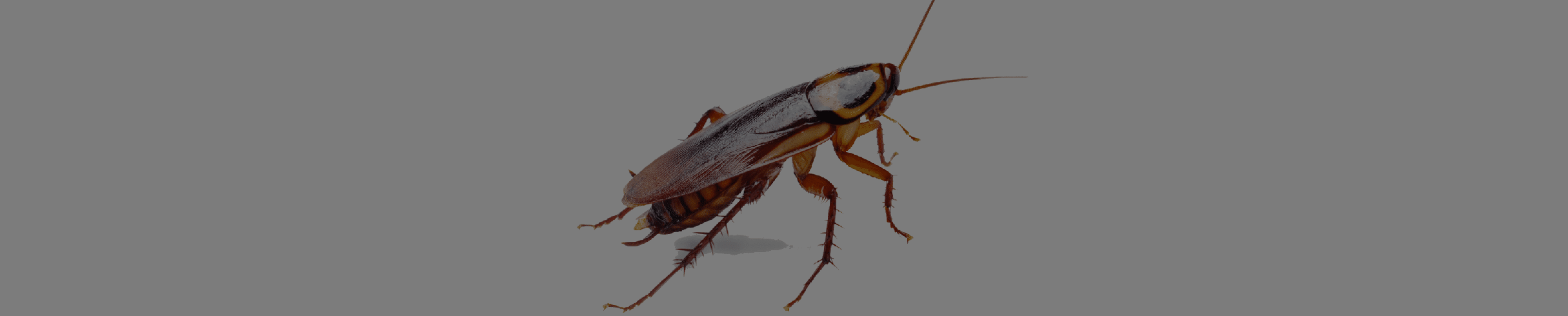
Cockroach

Cockroach Control: Our expert services target the main cockroach species found in South Florida, including German cockroaches, American cockroaches, and Brown-banded cockroaches. We provide comprehensive solutions to eliminate infestations and prevent their return.
Organic Solutions: We use professional organic products and methods to safely and effectively control cockroaches. Our approach ensures the safety of your family, pets, and the environment while effectively eliminating these pests.
Preventive Measures: In addition to eradicating existing infestations, we offer preventive solutions to keep cockroaches away from your property. Our services include sealing entry points, reducing food sources, and implementing regular monitoring.

Step-by-Step Process
1. Initial Consultation: Our process begins with a thorough consultation to understand your concerns and gather information about the cockroach infestation in your home or business.
2. Inspection: Our trained technicians conduct a detailed inspection to identify the extent of the infestation, focusing on common hiding places such as kitchens, bathrooms, and appliance areas. We look for signs of cockroaches, including live insects, egg cases, and droppings.
3. Identification: Accurate identification of the cockroach species is essential for effective treatment. We specialize in targeting the main cockroach species found in South Florida, including German cockroaches, American cockroaches, and Brown-banded cockroaches.
4. Customized Treatment Plan: Based on our findings, we develop a customized treatment plan using professional organic products. Our strategy includes targeted applications, baiting techniques, and growth regulators to disrupt the cockroaches’ lifecycle.
5. Treatment Implementation: Our technicians carefully implement the treatment plan, focusing on areas where cockroaches are most active. We use a combination of organic baits, dusts, and non-toxic insecticides to eliminate the infestation.
6. Follow-Up and Monitoring: After the initial treatment, we schedule follow-up visits to monitor the situation and ensure the complete eradication of the cockroaches. We make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan to achieve lasting results.
7. Prevention and Education: We provide expert advice and recommendations on how to maintain a cockroach-free environment. This includes tips on sanitation practices, proper food storage, and regular inspections to prevent future infestations.
Signs of a Cockroach Infestation
Florida’s climate is attractive to roaches, particularly the German cockroach and the brown-banded cockroach. The German cockroach, the most common type in the United States, can produce over 30,000 offspring in a single year. Spotting these pests can vary from seeing their shiny bodies and quick, spindly legs to hearing them rustling around at night.
They also emit a distinct odor from oily secretions, especially as their numbers increase. If you encounter this odor near food, it’s crucial to discard it, as there’s no safe way to salvage it. Additionally, you might come across their droppings, which resemble mouse droppings but can be distinguished by our professional team. These droppings may appear in the kitchen, pantry, or basement, where roaches often nest. Roach eggs, dark in color and enclosed in casings, can be found in various places, including inside food.
What’s even more unsettling is that cockroaches are resilient and challenging to eliminate through DIY methods. In such situations, it’s best to call in the experts at Pest Busterzz, your trusted pest control service. Our experienced exterminators are trained to swiftly and effectively remove cockroaches from your home. Contact us online to receive a FREE quote!
Different Cockroach Species in South Florida
German cockroaches, scientifically known as Blattella germanica, are one of the most common and troublesome species of cockroaches found worldwide. Here are some key points about their biology:
Appearance: German cockroaches are small in size, typically measuring about 1/2 to 5/8 inch (12 to 15 mm) in length. They have a light brown to tan color and are characterized by two dark parallel stripes running lengthwise on their pronotum (the shield-like structure behind the head).
Habitat: German cockroaches prefer warm and humid environments. They are commonly found in kitchens, bathrooms, and other areas where food, water, and shelter are readily available. They tend to hide in cracks, crevices, and secluded areas during the day, venturing out at night to forage for food and water.
Reproduction: German cockroaches have a high reproductive potential. A female German cockroach can produce multiple egg capsules (oothecae) in her lifetime, each containing around 30 to 40 eggs. The ootheca is carried by the female until the eggs are ready to hatch, after which the nymphs emerge.
Life cycle: The development of German cockroaches undergoes several stages. After hatching from the eggs, the nymphs go through multiple molts before reaching adulthood. The time from egg to adult can vary depending on environmental conditions, but it typically ranges from 2 to 4 months.
Feeding habits: German cockroaches are omnivorous scavengers and can feed on a wide range of organic matter. They have a particular affinity for starchy and sugary substances, but they also consume decaying matter, grease, and other food sources. They are known to contaminate food and food preparation surfaces with their feces, shed skins, and regurgitated material.
Health concerns: German cockroaches are not only a nuisance but also a potential health hazard. They can spread disease-causing bacteria, contaminate food, and trigger allergies or asthma in susceptible individuals. Their presence in residential or commercial settings should be addressed promptly to prevent infestations.
Understanding the biology of German cockroaches is essential for effective control and prevention. By targeting their hiding places, eliminating food and water sources, and employing appropriate pest control measures, it is possible to manage and eradicate German cockroach infestations.
“Palmetto bug” is a common term used to refer to the American cockroach (Periplaneta americana) in certain regions. Here are some key points about the biology of the American cockroach, often associated with the term “palmetto bug”
Appearance: American cockroaches are relatively large insects, measuring around 1.2 to 1.6 inches (30 to 40 mm) in length. They have a reddish-brown color and are characterized by a distinctive yellowish figure-eight pattern on their pronotum (the shield-like structure behind the head).
Habitat: American cockroaches are primarily outdoor insects but can also be found indoors in areas such as basements, sewers, and other damp and dark environments. They prefer warm and moist habitats, such as around drains, garbage areas, and decaying organic matter.
Reproduction: Female American cockroaches produce egg capsules (oothecae) that contain numerous eggs. Each capsule is typically carried by the female until it is ready to hatch. After hatching, the nymphs go through multiple molts before reaching adulthood.
Life cycle: The development of American cockroaches can take anywhere from 6 months to over a year, depending on various factors like temperature and food availability. They have a gradual metamorphosis, where the nymphs resemble smaller versions of the adults and go through several nymphal stages before becoming adults.
Feeding habits: American cockroaches are omnivorous and opportunistic feeders. They consume a wide variety of food sources, including decaying organic matter, garbage, food crumbs, pet food, and even other dead or injured insects. They are known to be particularly attracted to starchy and sweet substances.
Health concerns: American cockroaches can be potential carriers of disease-causing organisms such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites. They can contaminate food and food preparation surfaces, posing a risk to human health. Additionally, their shed skins and feces can trigger allergic reactions and asthma in sensitive individuals.
Understanding the biology of American cockroaches, commonly referred to as palmetto bugs, is crucial for effective control and prevention measures. By implementing proper sanitation practices, sealing entry points, and employing targeted pest control methods, infestations can be managed and their presence minimized.
The Smokybrown cockroach (Periplaneta fuliginosa) is a large species of cockroach known for its dark brown coloration. Here are some key points about the biology of the Smokybrown cockroach:
Appearance: Smokybrown cockroaches are larger than German cockroaches, with adults measuring about 1.25 to 1.5 inches (32 to 38 mm) in length. They have a dark brown to mahogany color and possess long antennae and wings that extend beyond the abdomen.
Habitat: Smokybrown cockroaches are primarily outdoor insects but can enter buildings and structures seeking shelter, especially in damp and dark areas. They prefer warm and humid environments and are commonly found in tree hollows, woodpiles, attics, and crawl spaces.
Reproduction: Female Smokybrown cockroaches produce egg capsules known as oothecae. Each ootheca contains around 15 to 20 eggs and is deposited in a safe location. After hatching, the nymphs go through several molts before reaching adulthood.
Life cycle: The development of Smokybrown cockroaches can take approximately six to 12 months, depending on environmental conditions. They have a gradual metamorphosis, with the nymphs resembling smaller versions of the adults. The nymphs molt several times before maturing into adults.
Feeding habits: Smokybrown cockroaches are omnivorous and feed on a wide range of organic materials. They consume plant matter, decaying organic matter, dead insects, and other organic debris. They are particularly attracted to plant materials, including leaves, fruits, and plant sap.
Behavior: Smokybrown cockroaches are primarily nocturnal, becoming active during the night to forage for food and water. They are agile climbers and are often found in elevated areas, such as trees or tall structures. They are not as commonly associated with human dwellings as some other species of cockroaches.
Understanding the biology and behavior of Smokybrown cockroaches is important for effective control and prevention measures. Proper sanitation practices, reducing outdoor harborage areas, and sealing entry points into buildings can help manage their presence and minimize potential infestations.
There are several natural repellents that may help deter cockroaches from entering your living space. While these methods may not completely eliminate an infestation, they can be used as supplementary measures alongside professional pest control methods. Here are a few natural repellents to consider:
Peppermint oil: Cockroaches are repelled by the strong scent of peppermint oil. Mix a few drops of peppermint oil with water in a spray bottle and apply it along baseboards, entry points, and areas prone to cockroach activity.
Catnip: Catnip contains a compound called nepetalactone, which acts as a natural repellent for cockroaches. Place small sachets of dried catnip in areas where cockroaches are commonly found.
Garlic: The pungent smell of garlic can deter cockroaches. Crush a few cloves of garlic and place them in strategic locations or create a garlic spray by mixing crushed garlic with water and spraying it around cockroach-infested areas.
Bay leaves: Cockroaches dislike the smell of bay leaves. Place whole bay leaves in cabinets, drawers, and other areas where cockroaches are active to help repel them.
Cucumber slices: Cockroaches are not fond of the odor emitted by cucumber. Place cucumber slices in areas where cockroaches are likely to hide, such as under sinks or in dark corners.
Remember that while these natural repellents may help keep cockroaches at bay, they may not be sufficient for complete control. For severe infestations, it is recommended to consult with a professional pest control service to ensure effective eradication and prevention.